5月 上
0501|1305. 两棵二叉搜索树中的所有元素
暴力解:
- 递归中序遍历,把结果全部写的 res 中,然后 sort 排序;
- 优化空间:见官方解法,
- 用 num1 和 nums2 分别拿到 root1 和 root2 中序遍历的结果,是递增的;
- 然后利用双指针 p1 和 p2 把 num1 和 num2 合并到 res 数组中。时间复杂度为 O(m+n)
var getAllElements = function (root1, root2) {
const res = [];
dfs(root1);
dfs(root2);
return res.sort((x, y) => x - y);
function dfs(node) {
if (!node) return node;
dfs(node.left);
res.push(node.val);
dfs(node.right);
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n+m) + nlogn ===> O(nlogn)
0502 | 591. 标签验证器
正则:
- 正则表达式不要背.
- 留个标记,winter 玩具浏览器 toy browser 可以按照这个思路优化。
1. 正则中 .*? 是什么意思?
.: 匹配 1 个字符,匹配 任何 单个字符;*:匹配 ≥ 0 个字符,匹配 在它之前的那个 字符。?:匹配 0|1 个字符,匹配 在它之前的那个 字符。
所以:
.*:匹配任何字符 ≥ 0 个;.?:匹配任何字符 0|1 个;
那么:
.*? : 匹配表示匹配任意字符到下一个符合条件的字符。
- 例子:正则表达式
a.*?xxx可以匹配abxxxaxxxxxabbbbbxxx。
.*:尽可能匹配符合条件的字符,尽可能长,贪婪模式
例子:
- 字符串:
<img src="test.jpg" width="60px" height="80px"/>如果要匹配 src 的属性值; src=".*", 匹配结果是:src="test.jpg" width="60px" height="80px"- 贪婪模式:意思是从
="往后匹配,直到最后一个",匹配结束。
- 贪婪模式:意思是从
src=".*?",匹配结果是:src="test.jpg"- 懒惰模式:匹配到第一个
"就结束了一次匹配,不会继续向后匹配。
- 懒惰模式:匹配到第一个
2. 正则中 [A-Z]{1,9} 是什么意思?
正则中的方括号
[]表示集合,也就是说只要字符串内容是 A-Z 中的任意大写字母都可以。正则中的大括号
{}表示次数,也就是匹配{}的前一个字符的次数:- {x} // x次
- {min, max} // 介于 min 次到 max 次之间
- {min, } // 至少 min 次
- {0, max} // 至多 max 次
- ? // 0|1 次
- * // ≥ 0 次, 也就是不限制次数,尽可能匹配最长
- + // ≥ 1 次/a{3}/表示匹配 a 3次
所以:原题目中的意思是匹配一个字符串,长度是 1-9 (含9) 个字符,这些字符必须是大写字母。
方法一:使用正则
var isValid = function (code) {
// cdata 内容
let reg1 = new RegExp(/<!\[CDATA\[.*?\]\]>|t/g);
// 开始、结束标签 \1 是一个回溯引用,引用了开始标签`<...>`的内容。
let reg2 = new RegExp(/<([A-Z]{1,9})>[^<]*<\/\1>/);
// 匹配cdata,然后置换为 - ;
code = code.replace(reg1, "-");
let temp = '';
while (temp != code) {
temp = code;
code = code.replace(reg2, "t");
console.log(code);
}
return code == 't';
};
方法二:使用状态机
- leetcode解析:链接.
- 栈 + 字符串遍历
var isValid = function (code) {
const n = code.length;
const tags = [];
let i = 0;
while (i < n) {
// 开始标签、结束标签、CDATA开头
if (code[i] === '<') {
if (i === n - 1) {
return false;
}
// 结束标签
if (code[i + 1] === '/') {
const j = code.indexOf('>', i);
if (j < 0) {
return false;
}
const tagname = code.slice(i + 2, j);
// 找到结束标签,让栈中的开始标签出栈,比对是否相等。
if (tags.length === 0 || tags[tags.length - 1] !== tagname) {
return false;
}
tags.pop();
i = j + 1;
if (tags.length === 0 && i !== n) {
return false;
}
// CDATA 内容
} else if (code[i + 1] === '!') {
if (tags.length === 0) {
return false;
}
if (i + 9 > n) {
return false;
}
const cdata = code.slice(i + 2, i + 9);
if ("[CDATA[" !== cdata) {
return false;
}
const j = code.indexOf("]]>", i);
if (j < 0) {
return false;
}
i = j + 1;
// 开始标签
} else {
const j = code.indexOf('>', i);
if (j < 0) {
return false;
}
const tagname = code.slice(i + 1, j);
// 判断开始标签是否符合长度 1-9 要求
if (tagname.length < 1 || tagname.length > 9) {
return false;
}
// 判断开始标签是否符合字母 A-Z 要求
for (let k = 0; k < tagname.length; ++k) {
if (!(tagname[k] >= 'A' && tagname[k] <= 'Z')) {
return false;
}
}
// 开始标签符合要求,写入 stack 中。
tags.push(tagname);
i = j + 1;
}
} else {
// 如果没有 '<' 则只有两种情况:
// 1. 处在一个开始标签內,且不在CDATA内:'<HTML> ......',这时候让 i++;
// 2. 不在一个开始标签内,'....<HTML>aaa</HTML>',这时候不符合标准,返回false。通过判断 tags.length 是否为0可以知道。
if (tags.length === 0) {
return false;
}
++i;
}
}
return tags.length === 0;
};
0503 | 937. 重新排列日志文件
对 sort 的灵活运用。
var reorderLogFiles = function (logs) {
// 保存 0 和 9 字母的code值
const ZERO = '0'.charCodeAt(0); // 48
const NINE = '9'.charCodeAt(0); // 57
// 原地排序
logs.sort((a, b) => {
// 判断是否为数字日志:dig开头。
// 思路:题干说“数字日志的所有字均由数字组成”,
// 所以:判断最后一个字符是否为数字。
const aDig = a.charCodeAt(a.length - 1) >= ZERO && a.charCodeAt(a.length - 1) <= NINE;
const bDig = b.charCodeAt(b.length - 1) >= ZERO && b.charCodeAt(b.length - 1) <= NINE;
// console.log(a, '->', aDig, '||', b, "->", bDig);
if (aDig && bDig) return 0; // 都是数字:保留相对位置
else if (aDig) return 1; // 如果只有a是数字,则a排在后面;反之亦然
else if (bDig) return -1;
// 都是false,都是字母日志:
// 由空格把 string 切割为 array :eg. "let1 art can" ==> ['let2', 'own', 'kit', 'dig']
const [aSp, bSp] = [a.split(" "), b.split(" ")];
// slice(1) 删去数组第一个成员,其为字母标识符。
// join(" ") 把 array 合并为 string。
// localeCompare 比较两个字符串,按照字典顺序谁应当排在前面。
const cmp = aSp.slice(1).join(" ").localeCompare(bSp.slice(1).join(" "));
// console.log(aSp, bSp, cmp);
if (cmp != 0) return cmp;
// 如果内容相同,则按照标识符排序
return aSp[0].localeCompare(bSp[0]);
})
return logs;
};
0504|1823. 找出游戏的获胜者
这道题使用队列也可以。
- 遍历 quene 时,从队尾拿出一个成员,然后再从对头插入。如此循环。
这里使用的是链表:
var findTheWinner = function (n, k) {
// 边界
if (k === 1) return n;
// 构造一个循环链表
const head = new TreeNode(1);
let point = head;
for (let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
point.next = new TreeNode(i);
point = point.next;
}
point.next = head;
// 循环
point = head;
while (point !== point.next) { // 当一个结点.next指向自己时,表明链表成员只有一个。
let pre = point; // pre 用于删除结点
for (let i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) { // 遍历,point 指向了待删除节点
pre = point;
point = point.next;
}
// 删除结点
pre.next = point.next;
point = pre.next;
}
return point.val;
// 创建一个结点
function TreeNode(val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
};
0505|713. 乘积小于 K 的子数组
- mid
- 滑动窗口。
求连续子树组的个数,“连续子树组”很强的暗示———使用滑动窗口。
本题只需记录 以每个数字为右边界所形成的有效子数组的个数 ==> right - left + 1 。
注意:
- 如果 k 为 <= 1 时,一定不存在有效结果,直接返回 0;
- 每次 while 循环,窗口因 right 都会向右扩展。
- 然后需要根据条件
count小于总数 k,通过移动 left 收缩左边界。 - 直到 count 满足条件,计算此时 "以 right 为右边界的有效子数组个数" ,累加到结果中。
- 然后需要根据条件
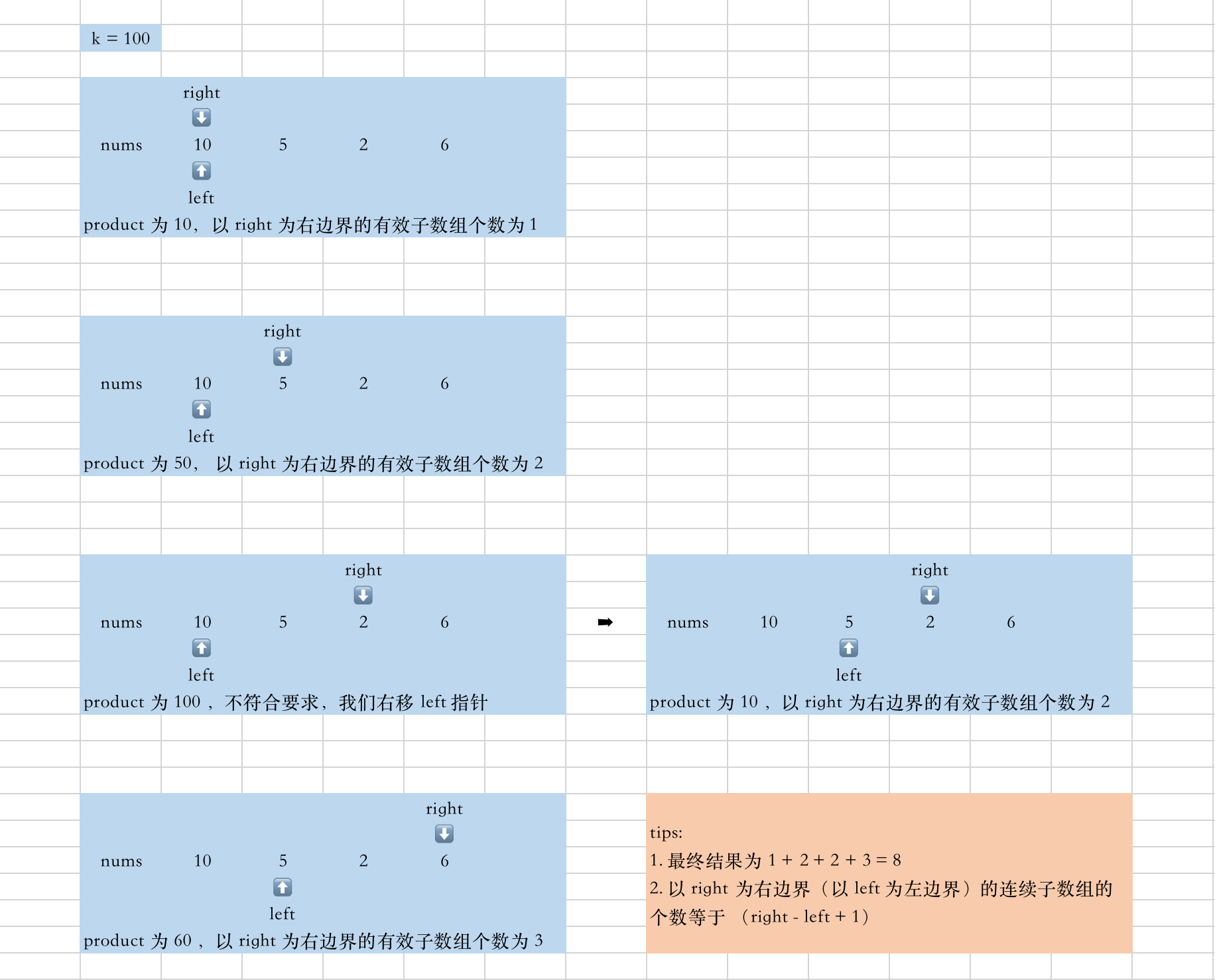
var numSubarrayProductLessThanK = function (nums, k) {
if (k <= 1) return 0;
// 滑动窗口:right
let res = 0;
let left = right = 0;
let count = 1;
while (right < nums.length) {
count *= nums[right];
// 不满足情况
while ( count >= k) {
count /= nums[left];
left++;
}
// 以 right 为右边界的有效子数组个数
res += right - left + 1;
right++;
}
return res;
};
❗️todo 看解析,学一下动态区间的模版,在这道题的题解里
0506|933. 最近的请求次数
- 队列的动态存储,不需要的值就及时抛弃(每次把超时的踢掉)
this的使用,原型链时间长了有点忘。
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:均摊 O(1),每个元素最多 入队 / 出队 各一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(L),L 为队列的元素个数。
var RecentCounter = function () {
this.queue = [];
};
RecentCounter.prototype.ping = function (t) {
this.queue.push(t);
while ( this.queue[0] < t - 3000 ) {
this.queue.shift();
}
return this.queue.length;
};
0507|433. 最小基因变化
- 一个 bfs / dfs 的应用题。
- 历年没考过,但思路不错。
方法一:bfs
const CHARS = ["A", "C", "G", "T"]
var minMutation = function (start, end, bank) {
const bankSet = new Set(bank);
const queue = [{ gene: start, step: 0 }];
// bfs
while (queue.length) {
const { gene, step } = queue.shift();
// 遍历单个基因: A, C, G, T
for (let i = 0; i < gene.length; i++) {
// 对每个基因进行替换,有3种替换方式
for (const nextChar of CHARS) {
if (gene !== nextChar) {
// 构建下一个基因序列
const next = gene.substring(0, i) + nextChar + gene.substring(i + 1);
// 下一个序列必须在基因库中,
if (bankSet.has(next)) {
// 返回结果
if (next === end) return step + 1;
// 已经使用过该基因,则从库中删去
bankSet.delete(next);
// 迭代:bfs
queue.push({ gene: next, step: step + 1 });
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
};
方法二:dfs
var minMutation = function (start, end, bank) {
// 基因库不存在目标基因
if (bank.indexOf(end) === -1) return -1;
// 可以进行的操作,如果基因段是 'A',则可以改变为 C,G,T,共3种基因字段。
const map = new Map([['A', 'CGT'], ['C', 'AGT'], ['G', 'ACT'], ['T', 'ACG']]);
// 基因库
const bankMap = new Set(bank);
// 基因发生变化的过程
const changeMap = new Set();
return dfs(start, end, 0);
// dfs: cur 当前基因序列
function dfs(cur, target, step) {
// 找到 target 返回结果
if (cur === target) return step;
// 找到 cur 变化的下一个基因序列(24种)
const nextStatus = getNextStatus(cur);
for (let nextStr of nextStatus) {
// 过滤:基因库中不存在该序列,或者与已经变化过的序列重复
if (!bankMap.has(nextStr) || changeMap.has(nextStr)) continue;
changeMap.add(nextStr);
// 递归: 深度遍历
const ans = dfs(nextStr, target, step + 1);
// 剪枝: 找不到有效的下一个基因序列,就及时结束递归
if (ans !== -1) return ans;
}
// 找不到一个有效的下一个基因序列
return -1;
}
// 获得当前基因序列的下一次变化序列(一共有24种可能性)。
// params: geneStr 当前基因序列
// return: <nextGeneStr>[]
function getNextStatus(geneStr) {
let geneArr = Array.from(geneStr), nextStatus = [];
// 遍历基因序列的每一个字母,列出所有可以能改变,一共有 3*8=24 种
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const temp = [...geneArr];
const nextChars = map.get(geneArr[i]); // 'A' -> 'CGT'
for (let j = 0; j < 3; j++) { // 遍历 'CGT'
temp[i] = nextChars[j]; // ['A','T','T'...] -> ['C','T','T'...]
nextStatus.push(temp.join('')); // --> .push('CTT...');
}
}
return nextStatus;
}
};
0508|442. 数组中重复的数据
方法一:set
遍历时,用 set 保存数据,当遍历到重复内容(set.has()),则 push 到结果中。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n);
var findDuplicates = function(nums) {
if (nums.length < 2) return [];
const set = new Set();
const res = [];
for (let n of nums) {
if (set.has(n)) res.push(n);
else set.add(n);
}
return res;
};
0509|942. 增减字符串匹配
贪心:根据提干规则,输入的 s 字符串长度为 n,输出的 perm 的长度就是 n + 1,
- 那么可以定义 perm 中所有 number 的范围为
[0, n]。其中min = 0, max = n; - 我们可以这样想,如果:
s[i] == 'I',那么只要perm[i]尽可能小就可满足条件,那只需要把当前最小的min放入即可,同时把min++;s[i] == 'D',同样的放入当前最大的值max即可,然后把max++;- perm 直到最后一个成员,此时
min和max已经相等,加入哪一个都可以。

- 时间复杂度:O(n);空间复杂度:O(1)
var diStringMatch = function (s) {
const len = s.length;
const res = [];
let [min, max] = [0, len];
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
res[i] = s[i] === 'I' ? min++ : max--;
}
res.push(min);
return res;
};
0510|1728. 猫和老鼠 II
太难,不做。
0511|449. 序列化和反序列化二叉搜索树
二叉树相关知识。
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历,会生成一个递增序列;
- 中序遍历 + 前序 / 后序遍历可以还原一个二叉树。
所以,当拥有一个二叉搜索树的后序遍历时,可以通过 sort 生成一个中序遍历序列,然后根据 中序 + 后序 的序列还原。
var serialize = function (root) {
if (!root) return "";
// 后序遍历
const res = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
// 根、左、右
res.push(node.val);
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
}
return res.reverse().join(',');
};
var deserialize = function (data) {
if (!data) return null;
const porder = data.split(',').map(item => parseInt(item));
const inorder = [...porder].sort((x, y) => x - y);
const len = porder.length;
return build(0, len - 1, 0, len - 1);
function build(inL, inR, poL, poR) {
// 边界
if (inL > inR) return null;
const root = new TreeNode();
root.val = porder[poR];
const index = inorder.indexOf(root.val);
const length = index - inL;
// 中序:左、根、右;[inL, inR]
// 后序:左、右、根;[poL, poR]
root.left = build(inL, index - 1, poL, poL + length - 1);
root.right = build(index + 1, inR, poL + length, poR - 1);
return root;
}
};
取巧:绕过了从序列构造二叉树的问题,直接用 JSON 相关 API 完成。
var serialize = function (root) {
return JSON.stringify(root);
};
var deserialize = function (data) {
return JSON.parse(data);
};
最终版本:
- 不需要再构造一个 中序遍历的序列,直接在 build 的时候判断即可:
- 因为可以唯一确定,所以我们只需要通过
stack.pop()不断拿出中序遍历的结果。- 结果是按照:左、右、根的顺序放入的。所以
stack.pop()拿出来的顺序自然是:根、左、右。每次拿出当前子树的根结点。 - 需要判断:当前要处理的根结点
stack[stack.length - 1]是否处在合理区间内:- 左子树的区间:
(root.val, right); - 右子树的区间:
(left, root.val);
- 左子树的区间:
- 如果符合区间,那可以确定当前处理节点应当放入对应子树下,否则证明对应子树下不再有节点,返回 null,判断下一个位置。
- 因为如果有节点,在按照后序遍历序列化时,一定要放在序列的这个位置。如果序列的这个位置没有符合条件的值(在合理区间内),那么说明原二叉树中的对应位置为 null。
- 结果是按照:左、右、根的顺序放入的。所以
var serialize = function (root) {
// [12,5,18,2,9,15,19,null,null,null,null,null,17]
if (!root) return "";
// 后序遍历
const res = [];
const stack = [root];
while (stack.length) {
const node = stack.pop();
// 根、左、右
res.push(node.val);
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
}
return res.reverse().join(',');
};
var deserialize = function (data) {
if (!data) return null;
// [2, 9, 5, 17, 15, 19, 18, 12]
const stack = data.split(',').map(item => parseInt(item));
const length = stack.length;
return construct(-Infinity, Infinity);
function construct(left, right) {
// 边界
if (stack.length === 0) return null;
// 要判断的当前插入的根结点在不在 (left, right) 区间内,不在返回null,位置不是这里。
if (stack[stack.length - 1] < left || stack[stack.length - 1] > right) return null;
const val = stack.pop(); // stack 中的顺序:根、右、左
const root = new TreeNode(val);
root.right = construct(val, right); // root.right.val > root.val 右子树要大,取值区间为 (val, right);
root.left = construct(left, val); // root.left.val < root.val 左子树要小,取值区间为 (left, val);
return root;
}
};
0512|944. 删列造序
解答思路:
var minDeletionSize = function(strs) {
const row = strs.length;
const col = strs[0].length;
let ans = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < col; ++j) {
for (let i = 1; i < row; ++i) {
// 直接比较同列上一个数字是否小即可,注意 i 从‘1’开始遍历
if (strs[i - 1][j] > strs[i][j]) {
ans++;
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
};
时间复杂度:O(m×n),其中 m 为字符串数组的长度,n 为数组中每个字符串的长度,判定每一列的的字典序需要遍历字符串数组每一列,因此时间复杂度为 O(m×n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
我的思路:
- 对按照列进行判断,那我们初始化一个保存每列情况的 list,并对 list 赋小于初始值 ‘a’ 的初始值。
- 然后双层 for 循环遍历成员,对每个数字按照自己对应的列来比较,如果符合预期(递增)就让 list 对应位置更新值,如果不如何预期,则对 list 对应位置赋 Inifinity。
- 最后,计算 list 中有几个 Inifinity,就证明有几个不符合条件。
var minDeletionSize = function (strs) {
let list = new Array(strs[0].length).fill('a'.charCodeAt() - 1);
for (let row = 0; row < strs.length; row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < strs[0].length; col++) {
if (strs[row][col].charCodeAt() < list[col]) list[col] = Infinity;
else list[col] = strs[row][col].charCodeAt();
}
}
return list.reduce((prev, curv) => {
if (curv === Infinity) return prev += 1;
return prev;
}, 0)
};
- 时间复杂度不变,空间需要额外维护一个长度为 m(每个单词的长度)的数组。
0515|812. 最大三角形面积
方法一:回溯算法,同时利用剪枝优化。
- 时间复杂度:参考回溯的时间复杂度。
var largestTriangleArea = function (points) {
let res = 0;
const len = points.length;
const path = [];
backtracking(0);
return res;
// 递归:每次传入 startIndex 确定下一次 for 循环的范围
function backtracking(startIndex) {
// 边界:当找到一个组合时,登记结果,结束递归。
if (path.length === 3) {
const [[x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]] = [path[0], path[1], path[2]];
res = Math.max(res, 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * (y2 - y3) + x2 * (y3 - y1) + x3 * (y1 - y2)));
return;
}
for (let i = startIndex; i < len - (3 - path.length) + 1 ; i++) {
path.push(points[i]);
backtracking(i + 1);
path.pop(points[i]);
}
}
};
方法二:暴力解
- 用三层 for 循环,虽然时间复杂度提升,但不需要额外的空间。
var largestTriangleArea = function(points) {
const n = points.length;
let ret = 0.0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
for (let k = j + 1; k < n; k++) {
ret = Math.max(ret, triangleArea(points[i][0], points[i][1], points[j][0], points[j][1], points[k][0], points[k][1]));
}
}
}
return ret;
};
const triangleArea = (x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3) => {
return 0.5 * Math.abs(x1 * y2 + x2 * y3 + x3 * y1 - x1 * y3 - x2 * y1 - x3 * y2);
}