5. 队列和栈
232. 用栈实现队列
- 232. 用栈实现队列
- 0508,easy,quick
方法一:
用两个栈 a 和 b 来模拟队列:
- 执行队列的放入时:
- b is empty, b 栈中的元素全部放到 a 中,让 b 为空;
- push 到 a;
- 执行队列的取出时:
- a is enpty, a 栈中的元素全部放到 b 中,让 a 为空;
- 从 b 中 pop;
- 原则:a 栈只能 push,b 栈只能pop。
var MyQueue = function () {
this.a = [], this.b = [];
};
MyQueue.prototype.push = function (x) {
const { a, b } = this;
// 把b清空
while (b.length) a.push(b.pop());
a.push(x);
};
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 把 a 清空
while (a.length) b.push(a.pop());
return b.pop();
};
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 把 a 清空
while (a.length) b.push(a.pop());
return b[b.length - 1];
};
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
return (!(a.length || b.length));
};
方法二:优化
- 总体思路不变, push 只能对 a 操作,pop 只能对 b 操作;
- push 时,直接 push 到 a 中,不需要先把 b 中的成员挪过 a 来。
- pop 时,需要判断 b 是否为空:
- 如果为空,则要把 a 中的所有成员挪到 b 中来,然后 b.pop();
- 如果不为空,则此时 b 栈顶的元素就是队列末尾的(即最先加入的)直接 pop 即可。
var MyQueue = function () {
this.a = [], this.b = [];
};
MyQueue.prototype.push = function (x) {
this.a.push(x);
};
MyQueue.prototype.pop = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 如果b中没有元素
while (!b.length) {
// 把 a 清空
while (a.length) b.push(a.pop());
}
return b.pop();
};
MyQueue.prototype.peek = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 如果b中没有元素
while (!b.length) {
// 把 a 清空
while (a.length) b.push(a.pop());
}
return b[b.length - 1];
};
MyQueue.prototype.empty = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
return (!(a.length || b.length));
};
225. 用队列实现栈
- 225. 用队列实现栈
- 0509,easy,normal
用 a 和 b 两个队列实现:
- 原则,必须有一个队列为空,也就是当 “栈” 存在数据时,两个队列一定是一个为空,另一个保存了全部数据;
- push:哪个队列有数据,就 push 到哪个队列中。
- pop:假设 a 有数据,那么 a 队列中我们要的数据在队头,也就是刚刚 push 进去的那个。此时需要循环执行
a.shift()把 a 的数据全部挪到 b 中,直到 a 只剩最后一个数据,然后返回最后一个数据即可。
- pop:假设 a 有数据,那么 a 队列中我们要的数据在队头,也就是刚刚 push 进去的那个。此时需要循环执行
- top:思路和 push 相同,最后一个数据在拿出来后,push 回 b 中即可。
var MyStack = function () {
this.a = [];
this.b = [];
};
MyStack.prototype.push = function (x) {
const { a, b } = this;
// a 和 b 哪个有数据,就往那个 push,默认往 a
b.length ? b.push(x) : a.push(x);
};
MyStack.prototype.pop = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 把有成员的队列清空,只留下最后一个 pop 出去
if (!a.length && !b.length) return null;
const [outStack, inStack] = a.length ? [a, b] : [b, a];
while (outStack.length > 1) {
inStack.push(outStack.shift());
}
return outStack.shift();
};
MyStack.prototype.top = function () {
const { a, b } = this;
// 把有成员的队列清空,只留下最后一个 pop 出去
if (!a.length && !b.length) return null;
const [outStack, inStack] = a.length ? [a, b] : [b, a];
while (outStack.length > 1) {
inStack.push(outStack.shift());
}
const res = outStack.shift();
inStack.push(res);
return res;
};
MyStack.prototype.empty = function () {
return this.a.length === 0 && this.b.length === 0;
};
20. 有效的括号
- 20. 有效的括号
- 0509,easy,quick
- 栈、map
方法一:传统
var isValid = function (s) {
const stack = [];
const left = ["(", "{", "["];
const right = [")", "}", "]"];
for (const char of s) {
// 如果是左括号,入栈
if (left.indexOf(char) !== -1) stack.push(char);
// 如果是右括号,出栈,判断是否匹配
else {
const l = stack.pop();
if (left.indexOf(l) !== right.indexOf(char)) return false;
}
}
return !stack.length;
}
方法二:map
var isValid = function (s) {
const stack = [],
map = new Map();
map.set("(", ")");
map.set("{", "}");
map.set("[", "]");
for (const char of s) {
if (map.has(char)) stack.push(char);
else if (map.get(stack.pop()) !== char) return false;
}
return !stack.length;
};
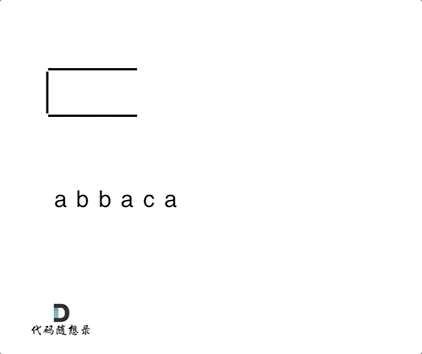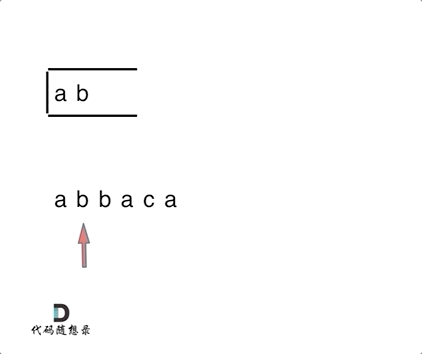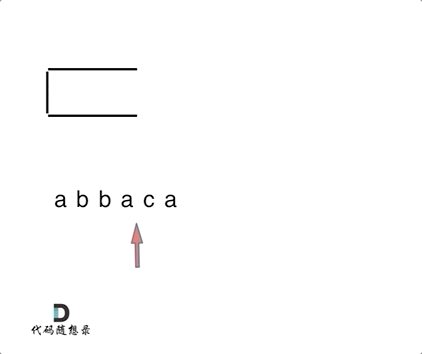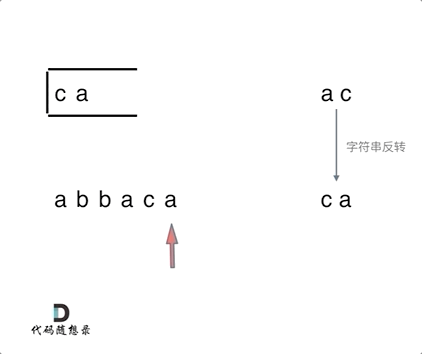
1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
- 1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
- 0510,easy,quick
- 栈
var removeDuplicates = function (s) {
if (s.length === 1) return s;
const stack = [];
const len = s.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 栈为空,直接放入
if (!stack.length) stack.push(s[i]);
// 栈不为空,拿出来判断
else {
stack[stack.length - 1] === s[i]
? stack.pop() // 如果相等,则取出来
: stack.push(s[i]); // 如果不相等,都放入
}
}
return stack.join("");
};
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 0510,mid,quick
- 栈
在 leetcode 的题干下方有对 逆波兰表达式 的解释,实际上该表达式就是一个栈结构的解析。
- 注意这里有一个 JavaScript 的坑,
/除法运算默认是保留小数的,这里我们通过Math.floor()可以做到结果 > 0 时的截断;- 但如果结果 < 0,为负数是,floor 向下取整不符合预期。比如结果为
Math.floor(-0.0423)的值为-1,而我们期望它做截断,结果为0。所以当结果为负数是,我们要求它向上取整Math.ceil()。
- 但如果结果 < 0,为负数是,floor 向下取整不符合预期。比如结果为
var evalRPN = function (tokens) {
if (tokens.length === 1) return tokens[0];
const stack = [];
const len = tokens.length;
const set = new Set(['+', '-', '*', '/']);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 运算符号
if (set.has(tokens[i])) {
const [y, x] = [stack.pop(), stack.pop()];
switch (tokens[i]) {
case '+': stack.push(x + y);
break;
case '-': stack.push(x - y);
break;
case '*': stack.push(x * y);
break;
case '/':
x < 0 && y < 0 || x > 0 && y > 0
? stack.push(Math.floor(x / y)) // 如果都为负数,则向上取整,floor
: stack.push(Math.ceil(x / y)); // 如果有且仅有一个为负,则向上取整,ceil
}
}
// 数字
else {
stack.push(Number(tokens[i]));
}
// console.log(stack, tokens[i]);
}
return stack[0];
};
239. 滑动窗口最大值
- 239. 滑动窗口最大值
- 0510,hard,normal
- 双端队列
维护一个单调递减的队列,代码随想录。
方法一:单调递减队列|保存下标
队列中保存的是下标。
一共有三种操作:
quene.push()操作。quene.shift()操作。res.push()操作。
var maxSlidingWindow = function (nums, k) {
const queue = []; // 双端队列, 保存索引
const res = [];
// 完整遍历一个滑动窗口
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//【push 操作】
// [push 1] 保证队列递减:如果队列中已经有值 且 新入列的值 >= 队列尾的值,则队列尾弹出
while (queue.length && nums[i] >= nums[queue[queue.length - 1]]) {
queue.pop();
}
// [push 2] 执行push
queue.push(i);
}
//【res.push】登记最大值
res.push(nums[queue[0]]);
// 遍历剩下的数
for (let i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
//【shift 操作】
// 判断队列首,是否要滑出滑动窗口
if (queue[0] <= i - k) queue.shift();
//【push 操作】
// [push 1] 保证队列递减:如果队列中已经有值 且 新入列的值 >= 队列尾的值,则队列尾弹出
while (queue.length && nums[i] >= nums[queue[queue.length - 1]]) {
queue.pop();
}
// [push 2] 执行push
queue.push(i);
//【res.push】登记最大值
res.push(nums[queue[0]]);
}
return res;
};
方法二:单调递减队列|保存值(不推荐)
队列保存的是具体的值。
var maxSlidingWindow = function (nums, k) {
let quene = []
const res = [];
// 前 k 个找 max
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// 当前数,值最大
if (quene[0] < nums[i]) {
quene = [nums[i]];
}
// 当前数,值不是最大,取出最大值
else {
while (quene[quene.length - 1] < nums[i]) quene.pop();
quene.push(nums[i]);
}
}
res.push(quene[0]);
for (let i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
// console.log('窗口出来的值', nums[i - k]);
// 当前数,值最大
if (quene[0] < nums[i]) {
quene = [nums[i]];
}
else {
// 当前数,值不是最大,取出即将出窗口的值
if (nums[i - k ] === quene[0]) quene.shift();
while (quene[quene.length - 1] < nums[i]) quene.pop();
quene.push(nums[i]);
}
res.push(quene[0]);
}
return res;
};
347. 前 K 个高频元素
- 347. 前 K 个高频元素
- 0510,mid,answer
- Map、小顶堆
总体思路,分两个步骤:
- 第一步:对 nums 数组中字符出现频率进行统计,用 map 保存。
- 第二步:取 map 中保存的 k 个字符,要求必须取频率最高的前 k 项。
第一个步骤没有什么好说的,直接 map 遍历一遍,时间复杂度:O(n);
第二个步骤就涉及到排序问题了,有两个思路:
- 方法一:转化为数组后用 sort 排序,转化数组 O(n),排序O(nlongn),总体的时间复杂度:O(n + nlogn) ==> O(nlogn)。
- 方法二:用小顶堆
方法一:sort 排序
var topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
// map 登记
const map = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.set(nums[i], (map.get(nums[i]) || 0) + 1);
}
// map 转换 为 array,会变成 [key, value] 组成的二位数组
// Map(3) { 1 => 3, 2 => 2, 3 => 1 } ==> [ [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 2 ], [ 3, 1 ] ]
const res = [...map].sort((x, y) => y[1] - x[1]).slice(0, k);
return res.map(item => item[0]);
};
方法二:小顶堆
解析地址.
- 坑。小顶堆 / 大顶堆 先跳过。
- 时间复杂度:遍历数组 O(n) ,一次堆化需要 O(logk) ,所以利用堆求 Top k 问题的时间复杂度为 O(nlogk); 空间复杂度:O(n)
let topKFrequent = function (nums, k) {
let map = new Map(), heap = [null,];
nums.map((num) => {
if (map.has(num)) map.set(num, map.get(num) + 1);
else map.set(num, 1);
})
// 如果元素数量小于等于 k
if (map.size <= k) {
return [...map.keys()];
}
// 如果元素数量大于 k,遍历map,构建小顶堆
let i = 0;
map.forEach((value, key) => {
if (i < k) {
// 取前k个建堆, 插入堆
heap.push(key);
// 原地建立前 k 堆
if (i === k - 1) buildHeap(heap, map, k);
} else if (map.get(heap[1]) < value) {
// 替换并堆化
heap[1] = key;
// 自上而下式堆化第一个元素
heapify(heap, map, k, 1);
}
i++;
})
// 删除heap中第一个元素
heap.shift();
return heap;
};
// 原地建堆,从后往前,自上而下式建小顶堆
function buildHeap(heap, map, k) {
console.log(map);
if (k === 1) return;
// 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,自上而下式堆化 ==> 非叶子结点: [1, Math.floor(k / 2)]
for (let i = Math.floor(k / 2); i >= 1; i--) {
heapify(heap, map, k, i);
}
}
// 堆化
function heapify(heap, map, k, root) {
// 自上而下式堆化
// while 循环的目的:以 root 为父节点的子树形成一个小顶堆,不断找到最小值 minIndex 交换位置到根结点。
while (true) {
let minIndex = root;
// 判断: 左子树存在,且左子树比父节点的值更小,minIndex 为左子树;
if (2 * root <= k && map.get(heap[2 * root]) < map.get(heap[root])) {
minIndex = 2 * root;
}
// 右子树
// 判断: 右子树存在,且右子树比父节点的值更小,minIndex 为右子树;
if (2 * root + 1 <= k && map.get(heap[2 * root + 1]) < map.get(heap[minIndex])) {
minIndex = 2 * root + 1;
}
// 如果左右子树中有节点比父节点更,那与父节点交换位置;
if (minIndex !== root) {
swap(heap, root, minIndex);
root = minIndex; // 重置root,让其一直指向最小值,也就是当前子树的根节点
} else {
break;
}
}
}
// 交换
function swap(arr, i, j) {
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
===== summary 1 =======================================
lodash
Lodash官网: lodash.com Lodash 中文文档: lodashjs.com
===== summary 2 =======================================
如何对一个 Map 进行按值排序?
- 转化为二维数组可以排序
- Map 是可迭代的,有
iterator,所以可以直接转化为二维数组。 - 然后利用
sort()对二维数组排序
const map = new Map();
// Map(3) { 1 => 3, 2 => 2, 3 => 1 },我们期望按照每一个成员的 value 大小进行排序
const arr = Array.from(map).sort((x, y) => y[1] - x[1]);
// [ [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 2 ], [ 3, 1 ] ]
===== summary 3 =======================================
坑:KMP 算法,小顶堆 / 大顶堆 的实现。